Comparison of Common Seed Allergens and Their Cross-Reactivity
| Seed | Major Allergens | Protein Family | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Cross-Reactive Foods | Severity of Cross-Reactivity |
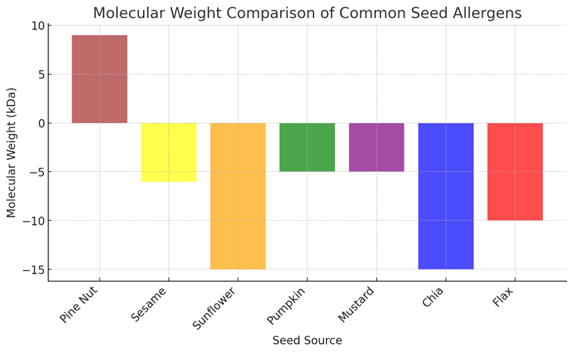
| Pine nut | Pin p 1, Pin p 3 | 2S Albumin, LTP | 9 | Tree nuts, Peanuts, Rosaceae Fruits | Moderate |
| Sesame | Ses i 1, Ses i 6 | 2S Albumin, Olesin | -6 | Peanuts, Tree nuts, Poppy seeds | High |
| Sunflower | Hel a 1, Hel a 3 | 2S Albumin, Vicilin | -15 | Tree nuts, Grass Pollen | Moderate |
| Pumpkin | Cuc m 2 | 2S Albumin | -5 | Tree nuts, Legumes | Low |
| Mustard | Sin a 1, Sin a 2 | 2S Albumin, LTP | -5 | Cruciferous Vegetables, Tree nuts | Moderate |
| Chia | Sal a 1 | Violin | -15 | Tree nuts, Legumes | Low |
| Flax | Lin u 1 | 2S Albumin | -10 | Tree nuts, Legumes | Low |
Molecular Weight Comparison of Common Seed Allergens
Comparison of Common Seed Allergens and Their Cross-Reactivity
The table and bar chart above compare the major allergens found in various seeds, focusing on protein family, molecular weight, and cross-reactivity severity.
Key Findings:
- Sesame Has the Highest Cross-Reactivity Risk
- Sesame (Ses i 1, Ses i 6) shares proteins with peanuts, tree nuts, and poppy seeds.
- Highly stable allergen, leading to severe reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Pine Nut Allergy is Linked to Tree Nuts and LTP Syndrome
- Contains 2S Albumin (Pin p 1) and Lipid Transfer Protein (Pin p 3).
- Cross-reacts with cashews, walnuts, and peaches/apples.
- Sunflower Allergy May Affect Tree Nut and Grass Pollen Allergy Patients
- Hel a 1 and Hel a 3 (Vicilin family proteins) are found in both sunflower seeds and tree nuts.
- Some cross-reactivity with grass pollen allergens.
- Mustard and Chia Seeds Show Moderate Cross-Reactivity
- Mustard (Sin a 1, Sin a 2) has some similarity to tree nuts and cruciferous vegetables.
- Chia and flax (Vicilin proteins) share minor cross-reactivity with legumes and tree nuts.
Cross-Reactivity Risk Assessment
| Seed Source | Major Allergens | Cross-Reactive Foods | Severity of Cross-Reactivity |
| Pine Nut (Pin p 1, Pin p 3) | 2S Albumin, LTP | Tree Nuts, Peanuts, Rosaceae Fruits | Moderate |
| Sesame (Ses i 1, Ses i 6) | 2S Albumin, Oleosin | Peanuts, Tree Nuts, Poppy Seeds | High |
| Sunflower (Hel a 1, Hel a 3) | 2S Albumin, Vicilin | Tree Nuts, Grass Pollen | Moderate |
| Pumpkin (Cuc m 2) | 2S Albumin | Tree Nuts, Legumes | Low |
| Mustard (Sin a 1, Sin a 2) | 2S Albumin, LTP | Cruciferous Vegetables, Tree Nuts | Moderate |
| Chia (Sal a 1) | Vicilin | Tree Nuts, Legumes | Low |
| Flax (Lin u 1) | 2S Albumin | Tree Nuts, Legumes | Low |
Clinical Implications for Seed Allergy Patients
Clinical Implications for Seed Allergy Patients
- Sesame Allergy is Closely Linked to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergies
- Often coexists with peanut allergies.
- Severe reactions possible, including anaphylaxis.
- Pine Nut Allergy Crosses Over with Tree Nuts and Fruit LTP Syndrome
- People with cashew or walnut allergy should be cautious.
- Rosaceae fruit (peach, apple) allergy sufferers may react to pine nuts.
- Sunflower Allergy is Rare but May Affect Pollen-Allergic Individuals
- Linked to tree nuts and grass pollen cross-reactivity.
- Symptoms range from mild to moderate.
- Mustard Allergy is Associated with Cruciferous Vegetables
- Includes broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts.
- Potential mild reactions in tree nut–allergic individuals.
